Is Elie Wiesel a perjurer?
Tuesday, August 24th, 2010
By Carolyn Yeager
Elie Wiesel stated under oath while giving testimony in the trial of Eric Hunt in San Francisco, California in July 2008 that the number A7713 was tattooed on his left arm. (see Where is the Tattoo? on this site)
Wiesel should have been asked to show his tattoo to the court at that time, but he wasn’t. This was a failure of the defense, for sure. But obviously, at that time, Mr. Hunt, the defendant, was not questioning whether Elie Wiesel had been an inmate of Auschwitz-Birkenau.
Since then, Mr. Hunt and others have uncovered video photography of Wiesel’s bare left arm from all angles, leaving no reasonable doubt that no tattoo is there. Backing up this conclusion is the fact that Wiesel has also famously refused to ever show his tattoo when requested to do so. For those who will retaliate that Wiesel may have had the tattoo removed, he said as late as March 25, 2010 that he still had the number A7713 on his arm. (see Where is the Tattoo?)
From this, the average man on the street would probably agree that Elie Wiesel has committed perjury (a criminal offense) if he does not indeed have the number tattooed on his arm. The law, according to http://www.lectlaw.com/def2/p032.htm, says:
When a person, having taken an oath before a competent tribunal, officer, or person, in any case in which a law of the U.S. authorizes an oath to be administered, that he will testify, declare, depose, or certify truly, or that any written testimony, declaration, deposition, or certificate by him subscribed, is true, willfully and contrary to such oath states or subscribes any material matter which he does not believe to be true; or in any declaration, certificate, verification, or statement under penalty of perjury, willfully subscribes as true any material matter which he does not believe to be true; (18 USC )
In order for a person to be found guilty of perjury the government must prove: the person testified under oath before [e.g., the grand jury]; at least one particular statement was false; and the person knew at the time the testimony was false.
However, in practice, the question of materiality is crucial. Perjury is defined at Criminal-law.freeadvice.com as:
the “willful and corrupt taking of a false oath in regard to a material matter in a judicial proceeding.” It is sometimes called “lying under oath;” that is, deliberately telling a lie in a courtroom proceeding after having taken an oath to tell the truth. It is important that the false statement be material to the case at hand—that it could affect the outcome of the case. It is not considered perjury, for example, to lie about your age, unless your age is a key factor in proving the case.
So the question becomes: Was the status of Elie Wiesel as a survivor of at least a seven-month incarceration at Auschwitz-Birkenau in 1944-45, in which case he would certainly have been tattooed on his left arm, as he states himself, material to the guilt or innocence of Eric Hunt in light of the charges that had been brought against him? Certainly, Eric Hunt, not long out of college at the time and who had been assigned to read Night in school, had come to doubt the truth of Wiesel’s assertions and descriptions in the book, and believed that if he could confront Wiesel alone, unguarded, he could convince him to tell the truth.
Does the suspicion that Wiesel necessarily lied in his book Night about what he saw and experienced at Auschwitz-Birkenau because he lied about the existence of a tattoo which he has always claimed as proof of his credentials as an Auschwitz survivor, exonerate Eric Hunt from some of the charges brought against him by the State of California? Is it material to the case? Perhaps not, but it does show cause for Eric Hunt’s desire to speak to Elie Wiesel in an unguarded moment, which was what he was attempting to do.
If Elie Wiesel cannot be legally found guilty of perjury because of questions of materiality, he will certainly be guilty of perjury in the eyes of the public if he does not produce the famous tattoo A-7713 on his arm—the sooner the better. We are waiting, Mr. Wiesel.
Watch a new, short video on the subject.
Addendum:
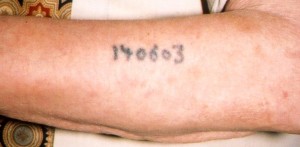 ”Auschwitz survivor Sam Rosenzweig displays his identification tattoo.” From Wikipedia According to the information below, this man was in the “regular” series—numbers not preceeded with a letter of the alphabet. Note also that the tattoo is on the outside of the left forearm.
”Auschwitz survivor Sam Rosenzweig displays his identification tattoo.” From Wikipedia According to the information below, this man was in the “regular” series—numbers not preceeded with a letter of the alphabet. Note also that the tattoo is on the outside of the left forearm.
This is the best looking tattoo I could find on the Internet. If you want to have your faith in the Auschwitz Holocaust story badly shaken, google “Auschwitz tattoos” (or any variation thereof) – Images, and see what comes up. Frightening! Of the little that is there, most look like the numbers are way too big, and you find the same few people exhibiting their specimen.
However … George Rosenthal, Trenton, NJ, an Auschwitz Survivor, has written an “authoritative” account at Jewish Virtual Library based on “documents” obtained from The United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. (Sorry, no pictures here either, or on the USHMM website. Elie Wiesel was a major driving force in the creationof the USHMM; why didn’t he volunteer his tattoo to be pictured on their website as an example of what a genuine tattoo looks like? Why does the USHMM have no images of a tattoo?)
Mr. Rosenthal writes:
The sequence according to which serial numbers were issued evolved over time. The numbering scheme was divided into “regular,” AU, Z, EH, A, and B series’. The “regular” series consisted of a consecutive numerical series that was used, in the early phase of the Auschwitz concentration camp, to identify Poles, Jews, and most other prisoners (all male). This series was used from May 1940-January 1945, although the population that it identified evolved over time. Following the introduction of other categories of prisoners into the camp, the numbering scheme became more complex. The “AU” series denoted Soviet prisoners of war, while the “Z” series (with the “Z” standing for the German word for Gypsy, Zigeuner) designated the Romany. These identifying letters preceded the tattooed serial numbers after they were instituted. “EH” designated prisoners that had been sent for “reeducation” (Erziehungshäftlinge).
In May 1944, numbers in the “A” series and the “B” series were first issued to Jewish prisoners, beginning with the men on May 13th and the women on May 16th. The “A” series was to be completed with 20,000; however an error led to the women being numbered to 25,378 before the “B” series was begun. The intention was to work through the entire alphabet with 20,000 numbers being issued in each letter series. In each series, men and women had their own separate numerical series, ostensibly beginning with number 1.
According to this, since there was never a “C” series, the maximum number of prisoners that could have been tattooed after May 1944 was 45,378.
Under “Notes” at the bottom of the page, four books are listed, all by holocaust historians. Are these the “documents” referred to? It also says Source: Center for Holocaust and Genocide Studies at the very bottom of the page, as if referring to the entire page. This Center is located at the University of Minnesota. The affiliated faculty reveals mostly Jewish names.
I report all this because I’m looking for authoritative sources for the exact placement of the tattoos on the left arm, but one doesn’t find that answer even at the Auschwitz-Birkenau Memorial Museum. Why all the uncertainty? Could it be because so many pseudo-survivors have tattooed themselves in unusual ways and places, and the authorities don’t want to nullify their legitimacy?
Category Featured | Tags: Tags: Auschwitz tattoos, Auschwitz-Birkenau Museum, Eric Hunt, George Rosenthal, perjury, Sam Rosenzweig, USHMM, Wiesel's non-tattoo,
Social Networks: Facebook, Twitter, Google Bookmarks, del.icio.us, StumbleUpon, Digg, Reddit, Posterous.