Blog
When did Elie Wiesel arrive at Auschwitz? Could he have received the number A-7713?
Written on January 19, 2012 at 7:19 pm, by Carolyn
By Carolyn Yeager
copyright 2012 carolyn yeager
Fact is–it’s a deliberately confusing story with two distinct versions. Originally, he was too late to be assigned that number; in a newer rewrite, he was right on time. Which would you believe?
Above: Hungarian transport arriving at Auschwitz-Birkenau in 1944. Notice the casual atmosphere, the inmate-workers in striped clothing (not wielding clubs), the non-threatening guards spotted here and there (without snarling dogs), and the crematorium chimney in the distance — which is not belching smoke and fire.
 UPDATE: (Jan. 30) It’s worth taking a closer look at the female deportees in the background who are accepting the arrival process in quite a different manner than what we always hear in the official stories of the Hungarian Jews. And from the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, I might add, which is a big pusher of the Hungarian Jewish “extermination.” These women don’t look too much the worse for wear from their trip. Three of them are smiling, two are also waving to someone they know, perhaps the person in the lower left questioning the officer. How can they be so cheerful, you might ask? A good question.
UPDATE: (Jan. 30) It’s worth taking a closer look at the female deportees in the background who are accepting the arrival process in quite a different manner than what we always hear in the official stories of the Hungarian Jews. And from the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, I might add, which is a big pusher of the Hungarian Jewish “extermination.” These women don’t look too much the worse for wear from their trip. Three of them are smiling, two are also waving to someone they know, perhaps the person in the lower left questioning the officer. How can they be so cheerful, you might ask? A good question.
______________________________
At the very end of my recent article The Truth About Night, I wrote:
My challenge: I welcome any native Polish Yiddish speaker/reader who is also fluent in English to prove me wrong about what I have written above by providing an honest, accurate translation of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign [And The World Remained Silent] into English so it can be compared with Night. Why hasn’t this already been done? It’s natural to be suspicious of what is kept hidden. Let’s put everything on the table so that the questions I have raised can be cleared up.
Though I had no real hope of that, I was most happily surprised when a gifted linguist using the name “Kladderadatsch” appeared on the Codoh Forum with a professional translation of a section from the Yiddish book. You can go to that thread (begin on page 4 of “Is This the End of Elie Wiesel?”) to see all the translations he has posted there so far. I have copied his last post/translation/analysis as the main element of this article, but first I want to give a short introductory comment.
When retranslating Night for its 2006 publication, Marion Wiesel (working with Elie and whoever else) made numerous changes in the wording of the original translation. An important, but hard-to-notice change was her rearrangement of the wording for the deportation dates of the Wiesel family. She connived to move their arrival date at Auschwtiz back two whole weeks. By doing so, she made it possible for young Eliezer to be given the registration number A-7713 on May 24, 1944, the day it was given out according to the transport records published by Randolph Braham1 and available at the Memorial Museum of Auschwitz-Birkenau. (More on Braham further down)
In the original LaNuit/Night published in 1958/60, and in Un di velt hot geshvign, published in 1956, the Wiesel family arrived at Auschwitz 3 days after their departure on June 3, 1944, making it approximately June 6th, well after the registration numbers A-7712 and 7713 had already been assigned. Therefore, as the story was originally written, the going-on-15-year-old Eliezer Wiesel could not have been registered with that number.
The analysis by ‘Kladderadatsch’ posted on Friday, Jan. 13:
Dates.
According to Mattogno, citing microfilm records from the Auschwitz museum (“Liste der Judentransporte, Museum of Auschwitz-Birkenau, microfilm no. 727/27,” Mattogno’s footnote 15), the Auschwitz registration number A-7713 was assigned on May 24, 1944. In his article, Mattogno makes the case that this means Elie Wiesel could not have been assigned A-7713 because he would have arrived at Auschwitz after that date:
Elie Wiesel does not specify the date of his deportation to Auschwitz. His narrative starts, though, with reference to a specific date: “On the Saturday before Pentecost [“Shavuòth” in the Italian edition], in the spring sunshine, people strolled, carefree and unheeding, through the swarming streets.” (p.22-23). In 1944, this festival fell on 28 May 1944 [14], a Sunday. The day in question was thus 27 May. The first transport of Jews left Sighet on the following day, hence, on 28 May. “Then, at last, at one o’clock in the afternoon, came the signal to leave” (p.27). Elie Wiesel then speaks of “Monday” (p. 29), the dawn (p.29), the day after tomorrow (p. 29) saying, at the end, “Saturday, the day of rest, was chosen for our expulsion” (p. 33) He then speaks about the traditional Friday evening meal and goes on to say: «The following morning, we marched to the station […]» (p. 33, which means that the trip to Auschwitz began on Saturday, 3 June 1944.
The duration of the trip is not given, but transports from Hungary usually took three or four days to reach Auschwitz-Birkenau. Elie Wiesel spent the night at Birkenau and was moved to Auschwitz the following day where he was given the number A-7713, which was tattooed on his arm (p. 54). Yet, according to him, “it was a beautiful April day” (p. 51).
This schedule is pure invention. If he did leave Sighet on 3 June 1944 he could not have arrived at Auschwitz in April. Moreover, the ID number A-7713 was given out on 24 May, the day on which 2,000 Hungarian Jews were assigned the numbers A-5729 through A-7728 [15]. According to Randolph L. Braham, a Jewish transport left Máramarossziget on 20 May 1944.[16] Allowing four days for the journey, this was the transport of Lázár Wiesel who was assigned the ID number A-7713 precisely on 24 May 1944. But apparently, Elie Wiesel was unaware of all these things.
[15] Liste der Judentransporte, Museum of Auschwitz-Birkenau, microfilm no. 727/27.
[16] R.L. Braham, A Magyar Holocaust. Gondolat Budapest-Blackburn International Inc.,Wilmington, 1988, p. 514.
That seems pretty conclusive.
On the other hand, however, Carolyn Yeager’s article about the various Wiesel signatures makes the case that Wiesel must have been deported from Sighet on May 20, 1944:
In the “revised and updated” new translation of 2006, Wiesel gives his family’s date of deportation to the “small ghetto” as May 17, 1944. I arrive at this date because Wiesel writes that it was “some two weeks before Shavuot” (Shavuot fell on May 28 in 1944) that the deportation order was announced to his family and neighbors. [Remember, Sighet had 90,000 residents, at least one-third of them Jews, while Wiesel makes it sound like he lived in a little village.] Departures were to take place “street by street” starting the next day. That would be May 15. But the Wiesel family was scheduled to leave in the 3rd group, which left two days later, on May 17. After being marched to the “small ghetto,” they stayed there “a few days.” On a “Saturday,” they boarded trains.5 The 20th of May, 1944 was a Saturday.
If Mattogno is correct that “transports from Hungary usually took three or four days to reach Auschwitz-Birkenau,” which seems probable, and if Wiesel’s transport departed on May 20, then it’s entirely possible for him to have arrived on May 23, spent the night at Birkenau, and then been marched over to Auschwitz on May 24 to get his prisoner number, A-7713 . . . exactly like Wiesel has always said.2
Now I’m pretty sure Carolyn wasn’t looking to prove that Wiesel’s claim to number A-7713 is legitimate (her focus in the article is actually on discrepancies in various arrest dates in the later Buchenwald paperwork), but if her reconstruction of the deportation’s timing is correct, that’s what she’s done.
So who’s right, Mattogno or Yeager?
Both, probably. The problem, of course, is that Wiesel is a moving target. Mattogno is using the original edition of “Night,” as translated by Stella Rodway. And sure enough, in that version it says “On the Saturday before Pentecost . . . ” But the “revised and updated” 2006 translation, which Carolyn quotes in her article, says “Some two weeks before Shavuot.” Since Pentecost and Shavuot are the same thing (Rodway just uses the more familiar term for non-Jewish readers, “Pentecost” being the name of a Christian holiday as well), that means that we have two possibilities:
1) Saturday before Pentecost/Shavuot,
2) an unspecified date “some two weeks before.”
As Mattogno and Yeager both note, Shavuot was on May 28 in 1944 (it’s easy to check), a Sunday. So counting backwards, “the Saturday before Pentecost” (May 28) gives May 27, and “two weeks before” gives May 14. In one case, the dates make it impossible for Elie Wiesel to have been assigned A-7713, in the other, they line up perfectly.
ing of 1945?
Above Left: Original Night, 1960, paperback. Right: Marion Wiesel’s 2006 new translation, recommended by Oprah Winfrey.
So here’s a situation where determining what the original text really says is important. Someone reading Mattogno’s article and then checking the most recent “revised and updated” edition of “Night” might just conclude that he’s dishonest–the text there doesn’t say “the Saturday before,” it says “some two weeks before.” Sheesh. And someone reading Carolyn’s article, with Mattogno’s in mind, might conclude that while she may start from the “correct” premises (again, according to the “revised and updated” version!), she really just shoots herself in the foot by proving that Wiesel left Sighet on May 20, exactly the right date for him to be on the transport recorded by Randolph Braham and to arrive in Auschwitz on May 24 to receive prisoner number A-7713. Is Mattogno lying? Can Carolyn not shoot straight?
Or could it just be that Wiesel is covering his tracks, sowing confusion among revisionists along the way?
“Un di Velt hot Geshwign,” p. 22:
Un azoy zenen teg farlofn, teg velkhe hobn aruntergerisn bleter fun kalendar un undz dernentert tsu yenem shwartsn shbth. Vos vet oyf eybik farbleybn in meyn zkhrwn, afilu ven ikh vel zeyn farmshpt tsu lebn bizn letstn tog fun ale teg, oyf der doziker tsby”wthdiker velt.
Geshen iz dos Shbth far Shbw”wth.
A friling-zun hot oysgegosn ir likht un varemkeyt iber der gorer velt un oykh iber geto. . . .
And so the days raced by, days which ripped away pages from the calendar and brought us nearer to that black Saturday [lit, black Sabbath]. Which will remain forever in my memory, even if I were condemned to live to the very last day of days on this deceiving world.
It happened Saturday [Sabbath] before Shavuot.
The springtime sun had spread its light and warmth over the whole world, and even over the ghetto. . . .
(Notice how he says he’ll never forget “that black Saturday” even if he was “condemned to live to the very last day of days.” I guess he might still mix the date up, though, right?)
Anyway, case closed? Well, there’s one last possibility. Jewish holidays are counted from the evening of the day before, and so maybe the Yiddish text is including Saturday, May 27 as part of Shavuot, thus making “Saturday before Shavuot” one week earlier, or May 20. But of course that still doesn’t fix the problem, since that date is just the starting point for the deportation process for the Jewish community: the Wiesel family isn’t relocated to the small ghetto until three days later, and not actually shipped out from Sighet until after several more. Which would mean, of course, that Elie Wiesel could not have been on the transport that left Sighet on May 20, and could not have arrived at Auschwitz by May 24 to receive prisoner number A-7713.
And somebody must have pointed that out to our friend Elie. So the whole thing gets wound backwards by two whole weeks. The text is quietly changed . . . and no one is supposed to notice.
Oh, and by the way, the original really does say “it was a beautiful April day”:
A sheyner April-tog iz es geven. A frilings-rich in der luft.
It was a beautiful April day. A scent of spring in the air.
“Un di Velt,” p. 83
Quietly changed, in 2006, to “It was a beautiful day in May.”
Do you suppose Elie reads Carlo Mattogno?
–end of post
Who is Randolph Braham and how credible is he?
Mattogno writes: “Moreover, the ID number A-7713 was given out on 24 May, the day on which 2,000 Hungarian Jews were assigned the numbers A-5729 through A-7728 [15]. According to Randolph L. Braham, a Jewish transport left Máramarossziget on 20 May 1944.[16] Allowing four days (or three-cy) for the journey, this was the transport of Lázár Wiesel who was assigned the ID number A-7713 precisely on 24 May 1944. But apparently, Elie Wiesel was unaware of all these things.”
[15] Liste der Judentransporte, Museum of Auschwitz-Birkenau, microfilm no. 727/27.
[16] R.L. Braham, A Magyar Holocaust. Gondolat Budapest-Blackburn International Inc., Wilmington, 1988, p. 514.
Braham is a Jewish Hungarian historian whose magnum opus, according to Arthur Butz, is his two-volume work The Politics of Genocide: The Holocaust in Hungary. Braham has written more on this subject than anyone else. The official story is that the entire Hungarian deportation program was carried out between May 15 and July 9, 1944. It started in Ruthenia (Carpatho-Ukraine, annexed from Slovakia) and northern Transylvania (annexed from Romania). The second location is where Sighet is found. A hundred thousand Jews remained in the hands of the Hungarians to be employed in labor battalions (in other words, were not deported).
The USHMM says this about him: Randolph L. Braham is Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Political Science and Director, Rosenthal Institute for Holocaust Studies, Graduate Center of the City University of New York, and Member, Academic Committee of the United States Holocaust Memorial Council. Publication of his two-volume work The Destruction of Hungarian Jewry: A Documentary Account (1963) distinguished Dr. Braham as a pioneer scholar in Holocaust Studies. He is coeditor (with Scott Miller) of The Nazis’ Last Victims: The Holocaust in Hungary (Wayne State University Press, published in association with the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, 1998) as well as author and editor of more than three dozen other works on the Holocaust in central and eastern Europe.
If Elie Wiesel is not prisoner #A-7713, then who is he and where was he between the spring of 1944 and the spring of 1945?
According to all available evidence, Elie Wiesel has falsely placed himself in the concentration camps Auschwitz I, II, III and Buchenwald by assuming the identity documents of Lazar Wiesel, born Sept. 4, 1913, as his own. This cannot be glossed over as a bureaucratic error because there are too many documents involved. Kenneth Waltzer, a professor of German history and Judaic Studies who has written about Elie Wiesel, has put forth this very explanation on this website and at Scrapbookpages Blog (although not on his own websites), but we haven’t heard a word from him in many months. He becomes quieter all the time.
It has been long remarked that Elie Wiesel’s book Night is fiction and does not accurately portray the camps wherein he claims to have been detained. This fictional story is based on a 245-page Yiddish book Un di velt hot geshvign (And the world remained silent), published in 1956 by a Yiddish publishing house in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Night, just 100 pages long, is a condensation of that book. The origins of Un di velt are not known at this time, but Elie Wiesel Cons The World will begin writing comparisons of the original and 2006 versions of Night – comparing them also with as much of the true original Un di velt as we can get hold of. It’s still a very interesting journey we’re on, but the end cannot be far away.
Endnotes:
1. Randolph L. Braham, The Politics of Genocide: The Holocaust in Hungary, two vols. (Boulder, Colorado: East European Monographs, 1993 [revised edition]).
2. In the original Night, it is actually the 2nd day after arrival that Wiesel writes he was tattooed. I will go into that in an upcoming article.
Nikolaus Grüner shows his tattoo. Where’s Elie’s?
Written on January 8, 2012 at 8:45 am, by Carolyn
By Carolyn Yeager
In this video, Nikolaus or Miklos (Michael) Grüner is being interviewed by the Modesto (Calif.) Bee while the photographer films him pointing out the tattoo on his left arm. This is shown in the very beginning of the video; right after that we see the famous “Buchenwald Liberation” photograph we’ve become so familiar with, and 16-year-old Grüner is in the lower left hand corner. Is Elie in the photo? No.
In 2008, Grüner traveled to California from his home in Sweden. While there, this very important bit of video was produced but has not been given the attention it deserves. I wonder why. Notice I didn’t form that as a question since I think the answer is apparent: If Grüner has a tattoo, why doesn’t Wiesel?
According to Elie Wiesel, he and his family were deported to Auschwitz in the same time period that Grüner and his family were–in May/June of 1944. They both tell a similar story of arrival at Auschwitz-Birkenau, the men being separated from the women whom they never saw again. After a period of adjustment, they were transferred to Monowitz-Buna where they lived and worked until January 1945, when both say they were transferred to Buchenwald. They also both say in their respective books that they were given a tattoo on their left forearm while at Birkenau – Wiesel the number A-7713 and Grüner A-11104.
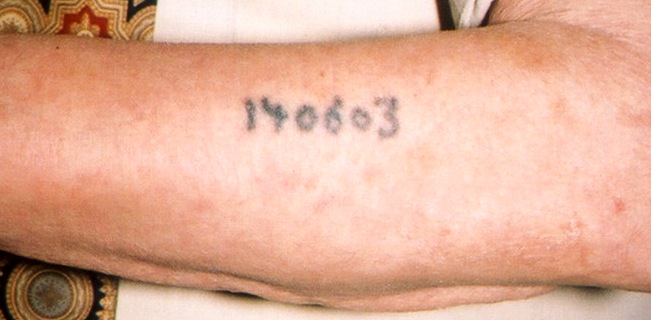 Gruner’s tattoo looks like a real tattoo to me. It looks very similar to the one in this picture at right of Sam Rosenzweig’s arm, which I have posted previously and is the best example of an Auschwitz tattoo I have found. According to George Rosenthal, writing for the Jewish Virtual Library, and accepted by the USHMM, Sam’s tattoo represents the “regular” series of numbers used at Auschwitz from 1940, while the “A” series was first issued in May 1944.
Gruner’s tattoo looks like a real tattoo to me. It looks very similar to the one in this picture at right of Sam Rosenzweig’s arm, which I have posted previously and is the best example of an Auschwitz tattoo I have found. According to George Rosenthal, writing for the Jewish Virtual Library, and accepted by the USHMM, Sam’s tattoo represents the “regular” series of numbers used at Auschwitz from 1940, while the “A” series was first issued in May 1944.
So we have evidence from Grüner and the photograph above of what Elie Wiesel should have on his arm, but doesn’t. There is no point in “Wiesel Believers” continuing to make excuses or look for reasons why their hero Elie won’t come clean about his bare arms. We know he has no tattoo where it is supposed to be … or anyplace! Just look at the top of this website. Or the photo below … from the 1996 documentary film “Elie Wiesel Goes Home.” We see his left arm in bright sunlight; clearly there is nothing on it. In the film we can see his right arm too, many times, which also has nothing on it. What more is there to be said? It’s a slam-dunk, and there is nary a word coming from the Wiesel camp about it. Isn’t it about time? Yes, but nothing happens unless people demand it.
Remember, on March 25, 2010 at the University of Dayton, a student asked Wiesel if he still has his concentration camp number and if it serves as a reminder of those terrible experiences. “I don’t need that to remember, I think about my past every day,” he responded. “But I still have it on my arm – A7713.
Robert A Brown, President of Boston University (Wiesel’s employer) wrote to me on Sept. 27, 2010, after receiving all this evidence, “I have no doubt that he is a survivor of the Holocaust and … a man of integrity and would not stoop to fabrication.“
What do you think?
Ten Questions for “Elie Wiesel Believers”
Written on January 4, 2012 at 10:34 am, by Carolyn
By Carolyn Yeager
10 “tricky” questions for those who believe Elie Wiesel was in Auschwitz and Buchenwald camps and that he wrote Un di velt hot geshvign (And the world remained silent) based on that experience.
On the CODOH Forum Friedrich Paul Berg started an interesting thread on Dec. 30 with the title “Ten Trick Questions for “Holocaust Survivors.” Berg writes that his questions
are not really tricky at all. They are simply the kinds of normal and reasonable questions that defense attorneys should always ask prosecution witnesses. However, we have all been so thoroughly programmed with holocaust propaganda that hardly anyone ever dares to ask the right questions.
Berg is quite right and it gave me the idea to create my own questions for those (even some revisionists) who insist that Elie Wiesel has to be the author of the Yiddish book published in 1956 in Argentina, and that I am oh so wrong in trying to prove otherwise.
Above is an image of Elie Wiesel in 1954, age 25-going-on-26, when he says he wrote Un di velt … attached to some kind of entry card issued by the Yugoslavian embassy in Paris.
So here are the questions I would like those ‘believers’ to answer. As Friedrich Paul Berg would say, they are normal and reasonable questions that attorneys should ask witnesses in court. Try your hand at answering them and send your answers to [email protected] or write them in a comment below. (Serious answers only, please)
1. Exactly when did Elie Wiesel write Un di velt hot geshvign? [not the year only, but the month(s), day(s)]
2. Exactly where was Elie Wiesel when he wrote Un di velt hot geshvign?
3. How many pages was the original draft of Un di velt hot geshvign?
4. How many pages was the finished, published book?
5. Who edited the book from the original draft?
6. Why didn’t Elie Wiesel make a carbon copy of his manuscript when he typed it? (This was the common practice at the time.)
7. Why didn’t Elie Wiesel tell Francois Mauriac during their meeting in May 1955 that he had already written his ‘testimony’ of being in the camps the year before?
8. Why did Elie Wiesel lie to Francois Mauriac and continue to lie to him?
9. Why has Un di velt hot geshvign never been translated into English or French, since it is the original source work of Night, which has sold an estimated 10 million copies worldwide?
10. Who holds the copyright on Un di velt hot geshvign?
The Truth about ‘Night’: Why it’s not Elie Wiesel’s Story
Written on December 23, 2011 at 4:59 pm, by Carolyn
by Carolyn Yeager
copyright 2011 carolyn yeager
 Why is Grandma Nisel not mentioned in Elie Wiesel’s Night?
Why is Grandma Nisel not mentioned in Elie Wiesel’s Night?
According to Hilda Wiesel’s 1995 “Survivors of the Shoah” testimony, Grandmother Nisel (also spelled Nissel) went with the family to Auschwitz.
According to Elie Wiesel’s 1995 memoir, All Rivers Run to the Sea1, Grandmother Nisel went with the family to Auschwitz.
But Grandma Nisel is not mentioned even once in Wiesel’s 1958-60 supposedly autobiographical Night.2
Did Wiesel simply forget about his grandmother only 10 years after the event and then remember her again in the 1990’s? Did he cut her out because he wanted to condense his book and she was peripheral to the storyline? Neither of these can be believed. In the first place, Wiesel makes it clear in All Rivers how important Grandma Nisel was to him and he writes affectionately about her. Secondly, by including his grandmother when he mentioned his mother and three sisters, he would not have added more than a few words to the deportation narrative, as we will see. Thirdly, Grandma Nisel, as a member of his family group that he says he lost at Auschwitz, could not with any decency be left out when writing about this momentous event.
And, in fact, he didn’t leave her out of his memoir, nor did Hilda leave her out of her testimony. But Night is another story (pun intended).
There is no excuse or explanation that can be given for such a lapse, and none has ever been attempted. Not one of Wiesel’s numerous interviewers, biographers, commentators or adulators have ever asked about it, or, if they did, they must have accepted without complaint a “no comment” from him. (I suspect that whenever Wiesel gives an interview or allows someone to write a book about him, he obtains an agreement in advance as to what can be discussed and what is off-limits. And I imagine probing questions about his family are off-limits … probably on the grounds that it is “too painful” for him. Wiesel is always treated with the softest of kid gloves.)
Who is Grandmother Nisel and why is she important?
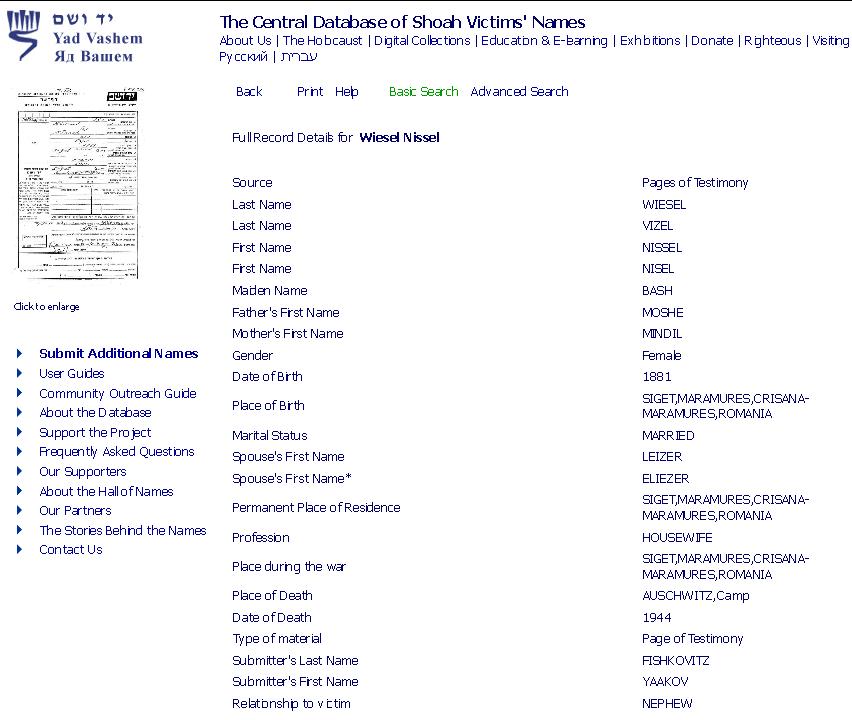
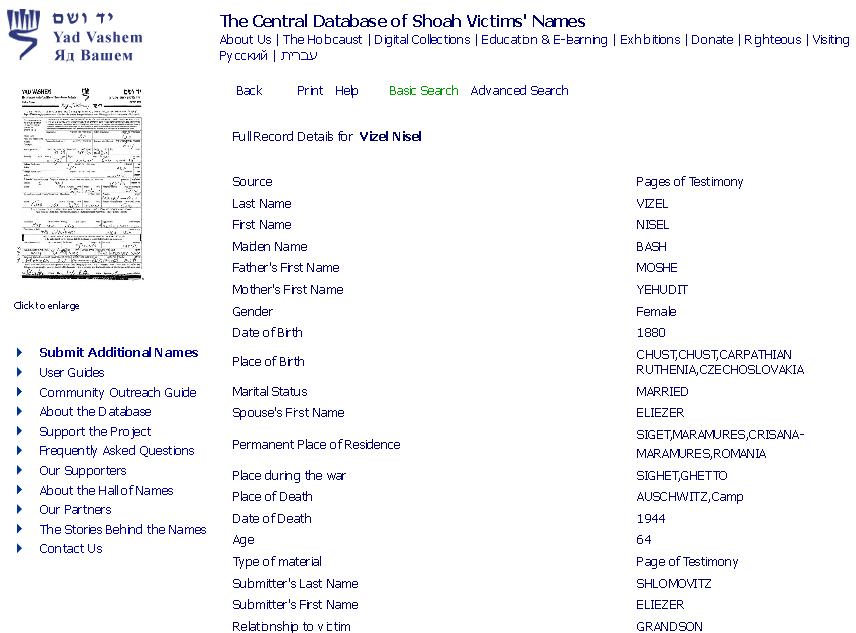
Nisel Bash was the daughter of Moshe and Yehudit (or Mindil) Bash (or Basch). She was born in 1881 in Chust, Ruthenian-Czechoslovakia. She married Eliezer Vizel and lived with him in Sighet, Rumania … which later became Hungary. (This information is from the victim forms filled out for Yad Vashem by her nephew and grandson; see further below.) We don’t know the date of her marriage, but her first child may have been born in 1900 when she was 19 years old. This first child of Nisel and Eliezer was probably a daughter, either Idiss or Giza. In 1903 their first son, named Shlomo, was born. After that came another son, Mendel; then two more daughters.
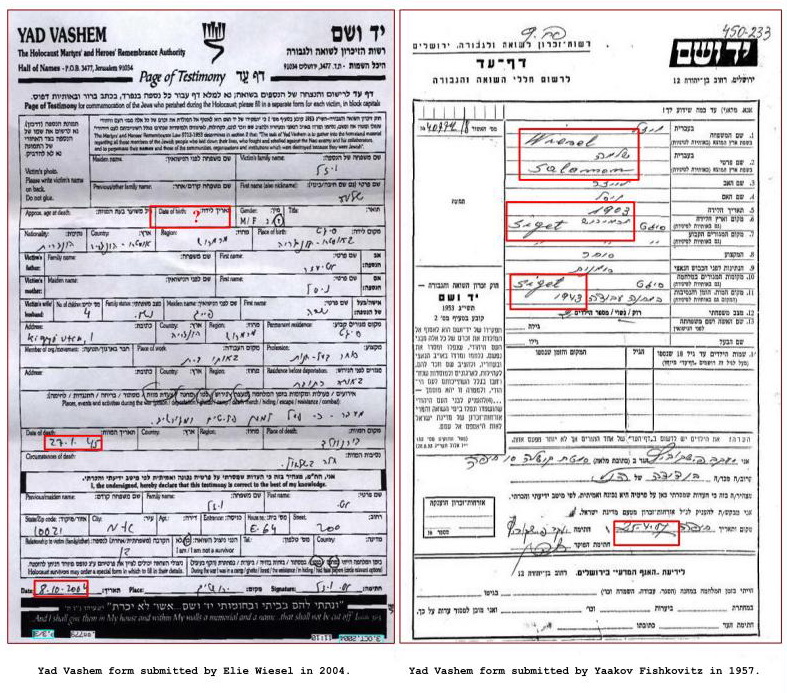
Below: YV forms for Shlomo Wiesel by Son Eli and cousin Yaakov Fishkovitz. (click on picture for larger image) Below that is the 1957 YV form for Mendel Wiesel by Yaakov Fishkovitz.
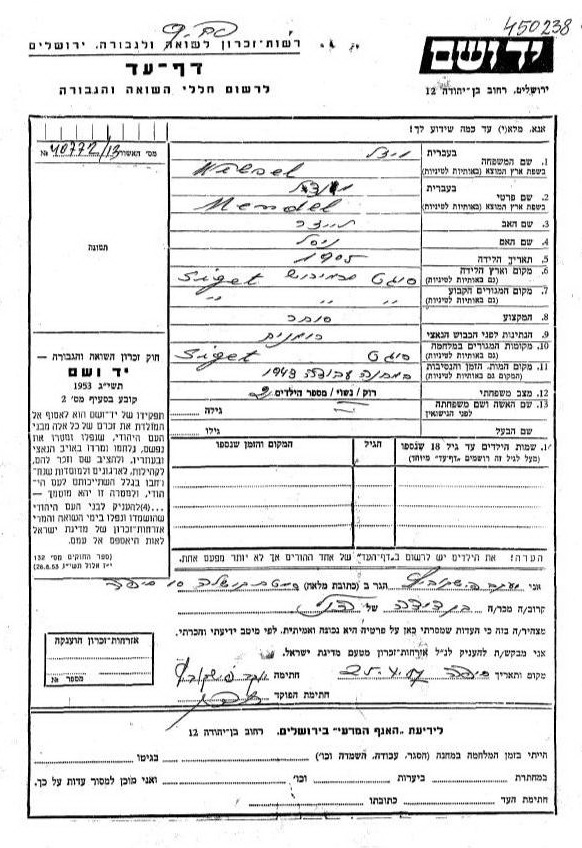 I have reconstructed the birth dates of Nisel’s children as best I can since no reliable family genealogy has ever been made available. Sites like Rootsweb are completely useless for information about the Wiesel family. In All Rivers (p. 7), Elie Wiesel writes about his aunts:
I have reconstructed the birth dates of Nisel’s children as best I can since no reliable family genealogy has ever been made available. Sites like Rootsweb are completely useless for information about the Wiesel family. In All Rivers (p. 7), Elie Wiesel writes about his aunts:
“I also had two aunts in Czechoslovakia: Aunt Idiss in Slotvino and Aunt Giza in Ungvaer. Grandma Nissel’s other two daughters lived in Sighet. Zlati, the youngest, was called an old maid behind her back. She married late, you see—at twenty-one.”
The older of the two daughters who lived in Sighet is never named or described, yet she could not have died as a child since Wiesel speaks of her as living in Sighet when he was a boy. Did she disgrace the family in some way and so is not to be mentioned? Wiesel writes that Grandma Nisel sat at the cash register in his father’s store, but also helped out at her son Mendel’s store:
“Maybe (Grandma Nisel) was trying not to show favoritism toward any of her children. My father was the oldest, but she was just as close to my Uncle Mendel, who had a modest grocery store on the other side of town.”
From this we can understand that Shlomo was the oldest of the two sons. Among Orthodox Hasidic Jews, males are in an entirely different category of importance and expectations than females, who are only required to find a good husband and have children. Mendel married Golda Feig, the sister of Sarah Feig, making for a tight-knit Wiesel-Feig family relationship.
Uncle Mendel Wiesel was born in 1905, according to cousin Yaakov (the only source we have) and died at the same time as Shlomo in 1943. He would have been only 38 years old! Yet in Night he appears in the story at the time of the deportation to Auschwitz—Elie Wiesel’s family stays in his empty house in the small ghetto. On page 30:
“The people must have been driven out unexpectedly. I went to see the rooms where my uncle’s family had lived. On the table there was a half-finished bowl of soup. There was a pie waiting to be put in the oven. Books were littered about on the floor. Perhaps my uncle had had dreams of taking them with him?”
Nisel lived in her own house that was close to her son Shlomo’s home. Young Elie dropped in often to visit her and had quite a few stories to tell about that in All Rivers. Elie’s namesake grandfather Eliezer had been killed in the First World War in his capacity as a stretcher-bearer. Nisel related to her grandson that when she was told of his death: “I learned what catastrophe meant, and I knew my mourning would never end.” (All Rivers, p 8)
On page 9, Wiesel relates a story that when he returned to Sighet as an adult, he first went to the cemetery to find his grandfather’s grave. He spoke to his grandfather’s spirit about the deportation to Auschwitz thus: “Did you know, Grandpa, that Grandma Nisel was the only one in the family, almost the only one in the whole community, who guessed it all? She knew she would never come home. She left this wretched town in her funeral dress. Yes, she wore her shroud under her black dress. She alone was ready.”
There are two other distinct mentions in All Rivers of his grandmother taking part in the deportation-to-Auschwitz process. On Page 70 he writes that on Tuesday, May 16, they were ordered out of their houses to be sent to the small ghetto. “There was another heat wave. My little sister was thirsty, and my grandmother too.” Page 77, arriving at Auschwitz: “I stared intently, trying desperately not to lose sight of my mother, my little sister with her hair of gold and sun, my grandmother, my older sisters.”
Yet in 20 pages in the book Night of detailed description of the pre-deportation events, the trip to Auschwitz and their arrival, there is no mention at all of a grandmother. Nowhere in the entire book is there a Grandma Nisel.
Other family members place Grandma Nisel at Auschwitz.
Her nephew Yaakov Fishkovitz in 1957 filled out a YV form (above top) stating she died at Auschwitz in 1944. Yaakov also filled out a form for his cousin Shlomo Wiesel. A grandson, Eliezer Shlomovitz of Los Angeles CA, filled out a Yad Vashem form for his grandmother Nisel Vizel too, many years later in 1994 or 1999 (hard to read), saying she died at Auschwitz in 1944 (above). But neither Elie nor his two surviving sisters acknowledged her death at Auschwitz in this way. Although Hilda said in her 1995 Shoah testimony: “… we were, myself and my sister, the one who was in Canada and is now deceased; my mother; my grandmother, that is my father’s mother; and, oh . . . my little 10-year old sister.”
 Hilda also said: “And my mother – died. She was 44 years old.” She then repeated: “And my little sister – dead at age 10.” These are assumed deaths. But if she is correct about her mother’s age in 1944, then Sarah Feig was born in 1900. Could she have been 3 years older than her husband, born in 1903 according to his cousin Yaakov? Possibly, even considering what we know about Hasidic marriages, wherein the groom is usually no more than one year older, or the same age, as the bride.3 But Hilda, being the eldest, should know her mother’s age. Right: Hilda, age 16, in 1938 with her mother Sarah Feig Wiesel, who would have been 38 in the picture if she were born in 1900.
Hilda also said: “And my mother – died. She was 44 years old.” She then repeated: “And my little sister – dead at age 10.” These are assumed deaths. But if she is correct about her mother’s age in 1944, then Sarah Feig was born in 1900. Could she have been 3 years older than her husband, born in 1903 according to his cousin Yaakov? Possibly, even considering what we know about Hasidic marriages, wherein the groom is usually no more than one year older, or the same age, as the bride.3 But Hilda, being the eldest, should know her mother’s age. Right: Hilda, age 16, in 1938 with her mother Sarah Feig Wiesel, who would have been 38 in the picture if she were born in 1900.
The name Shlomo appears only once in Night at the end.
On the very first page of this famous novel it is written: “My father was a cultured, rather unsentimental man.” Right here it would have been natural to write: My father, Shlomo Wiesel, was a cultured, rather unsentimental man. But no, and throughout the book this character continues to be known only as “my father,” until page 103-4 when another prisoner, Meir Katz, addresses him by his first name. In the original edition it is spelled Chlomo; in the 2006 translation, the spelling is changed to Shlomo. The name of Wiesel also occurs only once, on page 51:
We had already been eight days at Auschwitz. It was during roll call. We were not expecting anything except the sound of the bell which would announce the end of roll call. I suddenly heard someone passing between the rows asking, “Which of you is Wiesel of Sighet?
The man looking for us was a bespectacled little fellow with a wrinkled, wizened face. My father answered him.
“I’m Wiesel of Sighet.”
The little man looked at him for a long while, with his eyes narrowed.
“You don’t recognize me—you don’t recognize me. I’m a relative of yours. Stein. Have you forgotten me already? Stein! Stein of Antwerp. Reizel’s husband. Your wife was Reizel’s aunt. She often used to write to us … and such letters!”
Let’s remember there were many Wiesel’s (Vizel’s) in Sighet, a town with a large Jewish population. For example, there are three Mendel Wiesel’s from Sighet of around the same age in the Yad Vashem databank, and there are eight Shlomo Wiesel’s recorded as succumbing in the camps. This doesn’t include all the Wiesel’s with other first names! So we can expect that the man Stein would have used the first name too, or Wiesel would have asked Stein which Wiesel he was looking for. This seems like another avoidance of using the name Shlomo, but it is strange that both the first and last name were used one time only.
On page 2, the sisters are named:
There were four of us children: Hilda, the eldest; then Bea; I was the third, and the only son; the baby of the family was Tzipora.
In the original Night (p 31), the family servant, a Christian from a nearby village, is named Martha. In All Rivers, she becomes Maria, and the name in the 2006 re-translation of Night is changed to Maria. Okay, it could have been an error.
The dust jacket on an original, hard-bound copy of Night reads: “The adolescent Elisha and his family, among hundreds of thousands of Jews […] are cruelly deported …” Elisha is not the name of the main character in the book; it is Eliezer. The first time that name is used is on page 86: “Let’s hope that we shan’t regret it, Eliezer.” On page 92: “Don’t let yourself be overcome by sleep, Eliezer.” On page 96, Eliezer is addressed by his name twice by Juliek. On page 108: ”Eliezer … my son … bring me … a drop of coffee…” Then, again, on pages 109, 110 and 112. Why is he called Elisha on the dust jacket? Elisha is the name of the main character in Wiesel’s second novel, Dawn. A little mix-up there?
In Night, Father is 50 and little sister is seven.
In spring 1944, just arriving at Auschwitz, Eliezer’s father declares that he is fifty years of age. Eliezer says he is “not quite 15.” (p 40) In the new 2006 translation (p 30), Eliezer’s age is changed to “15” but the father’s “fifty” remains the same. “Not quite 15” doesn’t equate to Elie Wiesel, whose birthday is Sept. 30, 1928, so that was an oversight in Night. Or it can also be seen as a similar situation as with Tzipora’s age: Making the young victims even younger so they will appear more sympathetic to the reader, and making some adults older. Lying about their age is a tactic used by many “holocaust survivors” in their memoirs to explain how they escaped the “gas chamber.” Arguably, this could have been done by Sarah Wiesel for Tzipora too—claiming her to be 14 instead of 10, since in the story Night, Eliezer made himself out to be 18 (3 years older that he really was) and got away with it.
 Why is the father in Night fifty? Shlomo Wiesel was certainly somewhere between 40 and 44 years of age in 1944. Actually, according to his cousin Yaakov, he wasn’t even alive, having died in 1943! Moreover, Mendel died in 1943 also. One has to assume from this that they died together somehow. Yaakov filled out a form for Mendel at the same time as for Shlomo. The forms look exactly alike except for the different name and date of birth. Shlomo is shown to be born in 1903, Mendel in 1905. Keep in mind that in 1957 the book Night was not yet published in French or English and the name of Elie Wiesel was completely unknown, so Fishkowitz had no reason to lie to protect his relatives, as he might have had later.
Why is the father in Night fifty? Shlomo Wiesel was certainly somewhere between 40 and 44 years of age in 1944. Actually, according to his cousin Yaakov, he wasn’t even alive, having died in 1943! Moreover, Mendel died in 1943 also. One has to assume from this that they died together somehow. Yaakov filled out a form for Mendel at the same time as for Shlomo. The forms look exactly alike except for the different name and date of birth. Shlomo is shown to be born in 1903, Mendel in 1905. Keep in mind that in 1957 the book Night was not yet published in French or English and the name of Elie Wiesel was completely unknown, so Fishkowitz had no reason to lie to protect his relatives, as he might have had later.
Contrarily, on the Yad Vashem form Elie Wiesel filled out in 2004, no birth date is given for his father, nor the age at death. Did he not know? Is it possible for a son not to know his father’s age?
This photograph (left) of Shlomo Wiesel was taken in 1942 according to Hilda Wiesel. At this time he would have been 39 years old.
Further, we have no information on these details for Wiesel’s mother Sarah Feig either, and no family member (or anyone) ever filled out a YV Holocaust victim form for her or her youngest daughter who supposedly died with her at Auschwitz. (Can the reason be that they don’t want to record an age/birth date for either one?) But, as I wrote above, Hilda Wiesel Kudler said in her Shoah testimony that her mother was 44 years old when she died, and her youngest sister was ten. Is Hilda a reliable witness?
On page 30 of Night, Eliezer says: “I looked at my little sister Tzipora, her fair hair well combed, a red coat over her arm, a little girl of seven.” This is when the family was walking to the ‘small ghetto’ after being ordered out of their home in the spring of 1944, only a week or so before they arrived in Auschwitz. But Hilda said Tzipora was then ten years old. Which is correct? Or is neither? Some of my readers will tell me, “What does it matter?” Accuracy matters, because if a source is wrong in some things that can be determined as wrong, nothing from there should be depended upon.
Nowhere in All Rivers do we find Tzipora’s age given by Wiesel, even though he mentions her many times. He only wants us to know that she was young or “a child.” A ten-year-old girl is quite a bit more mature than a seven-year old. I venture to say she was given the age of seven in Night to make her appear more vulnerable, and her death even more of a barbaric crime. Also, if she were seven, there would be more reason to “exterminate” both mother and daughter, under the extermination thesis. But in truth, a 44-year-old-woman and her 10-year-old daughter could be quite useful in the labor force, and therefore could have gone on to meet some other fate. There may even be some private knowledge of that—which may be another reason no one has filled out a Yad Vashem Holocaust Victim report for these two, while two were filled out for 64- year-old Grandma Nisel.
That Shlomo Wiesel was 50 years old in 1944 can be ruled out by the fact that his mother was 64 years old in 1944, making her only 14 years older than a 50 year old. So this Father character cannot truly be the real Shlomo. The father is depicted as somewhat confused, a poor decision maker, and as having difficulty adjusting to camp life, both physically and psychologically. He appears more like a man of sixty. Eliezer is often shown to be his father’s caretaker. “My father … was running at my side, out of breath, at the end of his strength, at his wit’s end. I had no right to let myself die. What would he do without me? I was his only support.” (Night, p 90)
A fifteen-year-old with a gold crown?
How many 15-year-olds do you know who have a crown on a tooth already? Thirty-one-year-olds may, the age Lazar Wiesel was in 1944. Or the following story could be totally fabricated. Wiesel writes in Night that when he was transferred to Monowitz (Buna), he was given a physical and a dental exam. The dentist wanted to remove his gold crown; Eliezer talked him out of it. One day his work foreman, named Franek, noticed the gold and told Eliezer he wanted it. Eliezer resisted, but eventually, after suffering a series of abuses, gave up his gold tooth to Franek. In this story, he is called out for his dental appointment by his number, “A-7713.” (p 58) The number is used again on page 64 when the Kapo decides to give him a beating.
I felt the sweat run down my back.
“A-7713!”
I came forward.
Earlier, on page 51, the author wrote:
“The three “veterans,” with needles in their hands, engraved a number on our left arms. I became A-7713.”
Yet where is the number A-7713 on Elie Wiesel’s left arm?
At Buna, he worked in an electrical warehouse alongside some Polish civilians and a few French women After his beating by the Kapo, one of the French girls came over to him, “wiped his blood-stained forehead with her cool hand,” gave him a mournful smile and a bit of bread. Finally she spoke to him “in almost perfect German.” Several years later he recognized her in the Paris Metro, and prodded her memory. They went to a terrace café and she revealed to him that she was Jewish, from a religious family, and during the occupation she obtained forged papers and passed herself off as an Aryan. She was enlisted in “forced labor groups” and deported to Germany. That’s how she escaped the concentration camps.
These kinds of stories abound in Night and other holocaust-survivor books. No witnesses, no proofs, no names, just a bit of imagination. I will remind you again that the original Night was published in 1960 categorized as Judaica/Literature … in other words, fiction. When the new translation came out in 2006, it was changed to Autobiography/Jewish Interest. It is now an autobiography of Elie Wiesel, with his picture on the back cover and a special new Preface, written by him, which condemns the Germans and attempts to explain the changes he and his wife have made in the text.
Eliezer Wiesel is not necessarily Elie Wiesel
The author of the Yiddish book is Eliezer Wiesel. The author of Night is Elie Wiesel. There is only 2 years between the publication of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign in 1956 and the French La Nuit in 1958, but in that time the author’s name had changed. When did Elie start being called ‘Elie’ rather than Eliezer or Liezer or Lazar or something else? According to some of his biographers, it was when he was still living at home with his family. As we know, there were many Eliezer Wiesel’s (Vizel’s) in Sighet, let alone in Hungary, at the time. Un di Velt Hot Gesvign, however, was written in Polish Yiddish, or at least it was published in that language. The final version of the book of 245 pages was edited by Mark Turkov who specialized in Polish Yiddish. Where the story came from, we really don’t know. That’s the bottom line. We have the preposterous story told by Elie Wiesel of writing it in a ship’s cabin on his way to Brazil at a time that he was involved in a serious love affair and embarking on an important assignment for his newspaper. Equally preposterous is his claim to have handed an 862-page manuscript over to the stranger Turkov during a chance meeting on the ship, docked at Sao Paulo, without a copy for himself or a contract or any guarantee of return – just ‘good faith.’ Being an experienced journalist at that time, he would certainly have known better. Worse than that, he says he didn’t even believe when he gave it to him that Turkov would publish it. (All Rivers, p 240-41)
We make a leap of faith to believe that Eliezer Wiesel has to be Elie Wiesel. It should also be pointed out that these survivor stories were all the rage within the Yiddish-speaking communities at the time. There were many of them in circulation, even before they were published. Elie Wiesel had cousins in Argentina whom he visited while he was there in April-May 1954; he mentioned them in All Rivers.4 It’s very likely that he was introduced to these survivor stories, and Mark Turkov’s publishing house, through these relatives and their circle. Was he attracted to a particular story by an author with his own name, Eliezer Wiesel?
More unlikely stories
Wiesel tells us another unlikely story in All Rivers (p 277) that in Dec. 1955, back in Paris, he received a copy of the published book, edited down to 245 pages, in the mail from Turkov. There are no witnesses to this. He only mentions telling one close friend, Israel Adler, who took him out for a coffee by way of celebration.(!) Shortly after that he moved to the United States. It appears from his writings that Wiesel forgot all about the manuscript he gave to Turkov until the book came to him in the mail, but he does add on that page that “they never did send back the manuscript”—to give himself a reason for not having it and not being able to say what was actually in it.
In contradiction to this story is the one wherein Francois Mauriac, whom Wiesel first meets in Spring 1955, encourages him to write about his concentration camp experiences. He doesn’t tell Mauriac he has already done so, but acts like he will think about it, later accepting the guilt-ridden, elderly Catholic’s help in getting the book published. Wiesel writes in All Rivers, p 319, that he sent a manuscript of what became La Nuit (Night) to Mauriac one year later, in 1956.
In 1957, during my convalescence, I received good news from Francois Mauriac: Jerome Lindon of Editions de Minuit was going to publish La Nuit (Night). The letter of confirmation opened a new chapter in the book of commentaries that is my life.
Lindon didn’t like the orginal title: “And the World Remained Silent.” He preferred a biblical phrase, perhaps something from the Book of Jeremiah. But after discussing various suggestions, we settled on La Nuit. Lindon also wanted me to tighten the text, given to him by Mauriac, though I had already pruned and abridged it considerably.
The text was given to the French publisher by Mauriac. In the following lines he says that he, Elie, was the one who made the drastic cuts in the original manuscript. When?!
He proposed new cuts throughout, leading to significant differences in length among the successive versions. I had cut down the original manuscript from 862 pages to the 245 of the published Yiddish edition. Lindon edited La Nuit down to 178.
What a tissue of lies. Never before had Wiesel written about the Yiddish book, but now, in 1995, he relates that it was he who cut the 862 pages to 245. Such a prodigious task would certainly not have gone unremarked upon by him! And now it is the publisher Lindon who did the final editing to 178 pages. One wonders just what part Elie Wiesel played in this group effort?
Wiesel continues with an unconvincing “explanation” of why the book’s original ending was cut out, something that was made controversial by a certain Jewish scholar. He then says, “By the time Night was published in France, I was at work on another book.” This rendition of how such an important book came about is so sloppy and insulting to the intelligence of his readers that it speaks for itself.
Both the USHMM and Wikipedia have the dates wrong.
At the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum Elie Wiesel Timeline: From 1952, it says Wiesel interviewed Mauriac in 1954 (it was 1955) and that Wiesel finished his “900-page Yiddish manuscript” in Brazil in 1955 (it was 1954). I believe it is backwards on purpose, in order to fit Wiesel’s lies. But this is typical of the scholarship carried out at this totally Jewish-run, but partially government-funded museum. It reads:
1954
During an interview with the distinguished French writer, Francois Mauriac, Elie is persuaded to write about his experiences in the death camps.
1955
Elie Wiesel finishes a nearly 900-page manuscript in Yiddish while on assignment in Brazil. And the World Stayed Silent is published in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
1963
Elie Wiesel becomes an American citizen.
Wikipedia skips over the dates, doesn’t give any dates for the writing of the books because they don’t fit, but says that Wiesel moved to NYC in 1955.
“In 1955, Wiesel moved to New York City, having become a US citizen: due to injuries suffered in a traffic accident, he was forced to stay in New York past his visa’s expiration and was offered citizenship to resolve his status.”
Others say he moved to NYC in 1956. Since he was still in Paris in Dec.’55, one assumes he didn’t leave for the U.S. until Jan. ‘56. Wiesel nowhere gives a date, which is the reason for the confusion — his biographers have to guess. But, while he received a U.S. “green card” sometime after recovering from his accident, he did not become a citizen until 1963. Wikipedia is known to change its information on Wiesel without notice. For example, it now spells his father’s name Chlomo, whereas previously it was Shlomo.
Why did Wiesel start campaigning for the Nobel Prize the same year Mark Turkov died?
 Mark Turkov, the publisher of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign (And The World Remained Silent), died in 1983, the same year Wiesel’s supporters began their campaign to get him a Nobel Prize. It is a fact that Wiesel never spoke about the Yiddish book that was the precursor to Night until after Mark Turkov’s death. As I wrote in “The Shadowy Origins of Night, Part III,” this was the time Wiesel first began to speak of being the author of the Yiddish book, which he obliquely referred to in his Nobel Prize acceptance speech in 1986, when he said “the world did know and remained silent.”
Mark Turkov, the publisher of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign (And The World Remained Silent), died in 1983, the same year Wiesel’s supporters began their campaign to get him a Nobel Prize. It is a fact that Wiesel never spoke about the Yiddish book that was the precursor to Night until after Mark Turkov’s death. As I wrote in “The Shadowy Origins of Night, Part III,” this was the time Wiesel first began to speak of being the author of the Yiddish book, which he obliquely referred to in his Nobel Prize acceptance speech in 1986, when he said “the world did know and remained silent.”
Another reason for bringing the previously ignored Yiddish book into the light is that Buchenwald survivor Myklos Grüner began, in 1987, to claim that a different Eliezer Wiesel was the author of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign, thus making it necessary for the first time for Elie to explain just how it got written … by him. That he botched the explanation so badly in his memoir is no surprise to those who have studied the man. From the article mentioned above:
Grüner writes in his book Stolen Identity (p 50), “My work of research to find Lazar Wiesel born on the 4th of September 1913 started first in 1987, to establish contact with the Archives of Buchenwald.” He was also writing to politicians and newspapers in Sweden. This could not have failed to attract the notice of Elie Wiesel and his well-developed public relations network. Grüner tracked down Un di Velt Hot Gesvign as the original book from which Night was taken, and believed it was written by his friend Lazar Wiesel and stolen somehow by Elie. (p 43)
This could account for why Elie Wiesel suddenly began to speak and write about ‘his’ Yiddish book, published in Buenos Aires, Argentina in 1956. He deals with it in his memoir All Rivers, published in 1995, after Turkov and everyone else associated with it are dead. No witnesses.
Is it too far-fetched to believe that Turkov agreed to remain silent about the real author of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign, either by being bought off, threatened, or even voluntarily? And once Turkov was safely dead, Wiesel and his supporters could breathe more easily about claiming his authorship of the book.
It is a strange fact that the title Un di Velt Hot Gesvign (or, in English, And the World Remained Silent) does not appear on the long list of “books by Elie Wiesel” at the beginning of his memoir All Rivers, nor in the original or in the new 2006 translation of Night. It also does not appear in the complete list of his books at The Elie Wiesel Foundation for Humanity. It is, however, at the beginning of the list of his books on Wikipedia. Clearly, there is uncertainty about this book, perhaps a desire by publishers not to put down in writing something that could bring them a lawsuit … or perhaps a wish by Wiesel not to stimulate questions about that book.
Conclusions
1. The characters in Night are only loosely based on Elie Wiesel and his family. Therefore it can’t be called an autobiography.
2. Elie Wiesel is the author of Night, written in French with the assistance of his editor and probably Francois Mauriac, but he is probably not the author of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign.
3. Elie Wiesel made arrangement while in Brazil/Argentina for Mark Turkov to mail him the book by Eliezer Wiesel as soon as there was a hard copy, or his relatives mailed it to him. (Elie received a copy in Dec. 1955, according to himself, but the book was not available to the public until 1956.)
4. In the winter and spring of 1956, in the United States, Elie adapted the book to a shorter version in French, which he mailed to Francois Mauriac in Paris. He inserted the names of his family members and personalized it, especially in the beginning chapters.
5. The secrecy of the birth and death dates among Wiesel’s close relatives is to keep from contradicting what is written in Night, on which his fame and fortune truly rests. Without Night, Wiesel fades into just another Jewish-Zionist writer.
6. Elie Wiesel’s failure to correct and clarify details of his family history (especially birth and death dates of his parents, sisters and other close relatives), and of the writing and publication of Un di Velt and La Nuit, mirrors his refusal to show the number A-7713 that he says is tattooed on his left arm.
7. The essential purpose for securing a Nobel Prize for Wiesel, in literature or peace, was to solidify his reputation in light of the fragility of Night as the basis of that reputation. Nobel prize recipients are a protected species by the entire “global elite,” not just the Jews. Having himself falsely identified in the Buchenwald Liberation photo served the same purpose.
My challenge: I welcome any native Polish Yiddish speaker/reader who is also fluent in English to prove me wrong about what I have written above by providing an honest, accurate translation of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign into English so it can be compared with Night. Why hasn’t this already been done? It’s natural to be suspicious of what is kept hidden. Let’s put everything on the table so that the questions I have raised can be cleared up.
Endnotes:
1. Elie Wiesel, Memoirs: All Rivers Run to the Sea, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1995. 418 pp.
2. Elie Wiesel, Night, Hill and Wang, New York, 1960. 116 pp. (Original edition)
3. “One day my father saw a beautiful young girl in a carriage and was so struck by her that he ran after her, calling out, ‘Who are you?’ Of course, she did not deign to reply, but that evening the driver gave him the answer. The girl was the younger daughter of Reb Dodye Feig, of the village of Bichkev. The following year they were married, and they had four children, three girls and a boy.” (All Rivers, p 15)
4. “In Buenos Aires my cousins Voicsi and her husband Moishe-Hersh Genuth came to meet us. I gave them some articles for Yedioth Ahronoth, unaware they would be reprinted or quoted in the American Jewish press.” (All Rivers, p 241)
Komisarjevsky Jury Didn’t Take Elie Wiesel’s Advice
Written on December 10, 2011 at 12:36 pm, by Carolyn
By Carolyn Yeager
Jury decides that death is the answer.
On Friday, December 9, the jury deciding the fate of home-invasion rapist/murderer Joshua Komisarjevsky rejected mitigating circumstances presented to them by Defense Council and decided for death on all 6 counts. This was hailed by the general public (as noted in immediate comments to newspaper stories1), while it was a disappointment to the state of Connecticut’s largest newspaper The Hartford Courant, some Connecticut lawmakers and Elie Wiesel.
 Above: Dr. William Petit, sole survivor of the brutal 2007 home invasion by Stephen Hayes and Joshua Komisarjevsky that took the lives of his wife and two daughters, watches as his sister Johanna Chapman thanks the jurors for taking their time to come to the “right decision” in this painful and disturbing case. Chapman attended all the court sessions with her brother.
Above: Dr. William Petit, sole survivor of the brutal 2007 home invasion by Stephen Hayes and Joshua Komisarjevsky that took the lives of his wife and two daughters, watches as his sister Johanna Chapman thanks the jurors for taking their time to come to the “right decision” in this painful and disturbing case. Chapman attended all the court sessions with her brother.
Left: The father of murdered Jennifer Petit, Rev. Richard Hawke. on left, embraces Christopher Komisarjevsky (right), the uncle of Joshua Komisarjevsky, outside the courtroom after the verdict was read. The elder Komisarjevsky, who strongly resembles Nikita Khrushchev in this profile pose, has written that his father, Theodore Komisarjevsky, was a renowned theater director from a famous Russian theatrical family. His mother was a leading figure in modern dance, a teacher and a writer. He, himself, is the former chief executive of the prominent public relations firm Burson-Marsteller. Joshua Komisarjevsky was adopted as an infant by Christopher’s brother Benedict; mother unknown. Christopher was the only family member to attend the sentencing trial, during which time he made friends with the Hawke and Petit families.
On Oct. 26, 2010, Wiesel made a speech in Connecticut while the trial for Steven Hayes was in session, calling on the jury to not give the death penalty to either Hayes or Komisarjevsky for their brutal torture/killing spree. In his speech Wiesel repeated the words “Death is not the answer.” I posted this article about it in October on Elie Wiesel Cons The World.
In that speech at Wesleyan University in Middletown, Conn. (which was organized by the B’nai B’rith Lecture Bureau, by the way, as are most of his public appearances), Wiesel indulged in his usual vague, high-sounding rhetoric. Lines such as “Moral societies should not be the agents of death” and “Death should never be the answer in a civilized society” flowed from his lips. This was his first direct address on capital punishment in the U.S., and it was a last minute change of topic, apparently when he and his handlers realized the widely publicized murder trial was underway nearby.
Wiesel: Death penalty can’t bring them back
Earlier in the day, while addressing the media, Wiesel spoke more directly about the case, acknowledging he had no business butting in … but did so anyway. “It would be almost obscene for me to comment about morality to the father,” Wiesel said. “I would only ask, do you really think that death could bring them back to life?” How insulting to William Petit, the father and lone survivor, to imply that his wish for the perpetrators to be put to death was because that would somehow bring his loved ones back to life. I would wager that Dr. Petit’s IQ and reasoning powers are above Wiesel’s and he understands the purpose for the death penalty is deterrence and justice appropriate to the crime—the latter being a concept that Wiesel reserves for Jews only.
Wiesel then made the ludicrous comment that he might change his stance if the death penalty could bring back victims. Knowing that no punishment can bring people back from death, this is a dishonest argument against the death penalty.
He went on to say: “It is not easy, but a civilized society needs to face such challenges. That father deserves a different language. We must find the words, the proper words, to deal with it.” Of course, he doesn’t come up with them. Wiesel is famous for failing to adequately explain or describe his claims and statements, and blaming it on language itself!
Even some Jews are unhappy with Elie Wiesel in this instance. On an Orthodox Jewish website, the comments were overwhelmingly against his interference, and his position, in the case. One commenter (#22) said simply, “Elie Wiesel is CREATING anti-Semitism by his sticking his nose in this case.”
The anti-death penalty campaign
An editorial by the liberal and Jewish-owned Hartford Courant immediately after the death sentence was passed quoted Elie Wiesel’s words from a year ago calling for the abolition of the death penalty. In a Dec. 9 editorial titled “With the Cheshire trials over, let’s stop sending people to death row,” they quoted an earlier editorial in which they stated:
We believe the better answer is to repeal the death penalty as immoral and bad public policy. Speaking at Wesleyan University last year, Nobel Peace laureate Elie Wiesel, who lost his parents and sister in the Holocaust, said moral societies should not be the agents of death. We aspire to be a moral society.
What hollow words coming from any mainstream media outlet in the United States! They aspire to be moral? The U.S. mainstream media generally refuses to do the moral thing. The Hartford Courant is part of The Tribune Company, which is owned by Sam Zell (aka Zielonka) whose Jewish parents immigrated to the U.S. from Poland in 1939. It’s not surprising, therefore, that it presents Elie Wiesel to it’s readers as someone whose words are important and should be heeded.
But I also want to respond to the Courant’s above statement by saying, once again, that we do not know for sure what became of Wiesel’s parents and sister. There is no solid evidence that they were “lost in the Holocaust”—only the statements of belief by family members. I realize that most people are shocked by a statement like that from me, but it is the truth. The Courant editorial goes on to give their reasons for wanting life imprisonment over the death sentence:
The two men were willing to plead to sentences of life in prison without possibility of parole. Because of the lengthy delays built into Connecticut’s death penalty, they will most likely serve life without parole. The trial becomes just a ritual in Connecticut death penalty cases, a kabuki play about justice instead of actual justice.
The Courant brings up unnamed “studies” in Maryland, North Carolina and New Jersey that found evidence that “killers of white victims are more likely to be sentenced to death than killers of nonwhite victims.” They don’t tell us the race of the killers, only of the victims. But the killers are probably overwhelmingly nonwhite. It also doesn’t tell us the nature of the killings, i.e. whether the crimes that received the death penalty contained aggravating circumstances that the others didn’t.
The Courant also argues the death penalty is too expensive. Finally, they argue the death penalty is about revenge. These are the identical arguments put forth by the Connecticut Network to Abolish the Death Penalty (CNADP). Who do you think is behind it? On their website, they state:
The death penalty is poor public policy. The death penalty does not deter crime, it is not cost efficient, it kills the mentally ill, it is economically and racially biased, it kills the innocent, and it does not provide closure to families – it is simply revenge, not justice.
I disagree. I believe the death penalty, especially if it were really carried out as it should be (within two years at the most) is a deterrent to the most gruesome capitol crimes … which are sadly becoming more common. As someone who lost his 19-year old daughter to a murderer correctly put it in an earlier Courant editorial:
The problem with the death penalty, as it is currently constituted, is that it is not carried out swiftly. There are murderers on death row who have been there for more than two decades. Their appeals are mainly stalling tactics as they offer no new evidence to claim innocence.
Elie Wiesel is wrong, and thankfully the jury for the Komisarjevsky sentencing phase thought so too. Long live the Jury System.
1. A Hartford Courant poll, as of 10 p.m. Dec. 9 with 660 votes so far, was running 86% in favor of the death penalty and only 13% opposed. Abolishing the death penalty is just another one of those fuzzy, wuzzy ideas being pushed onto average, normal Americans by the globalist ruling elite.