Posted on February 13, 2013 at 8:22 am
The Max Hamburger Story – Some Reasons Not To Believe It
by Carolyn Yeager
The interview with psychiatrist Max Hamburger that appeared in the March 2012 Dutch magazine Aanspraak was translated into English for me by Hasso Castrup. Some things that Hamburger said are revealing of his overall honesty when it comes to his statements about “the Holocaust.” Being a “holocaust survivor” who appears in the famous photograph is, after all, his only claim to fame.
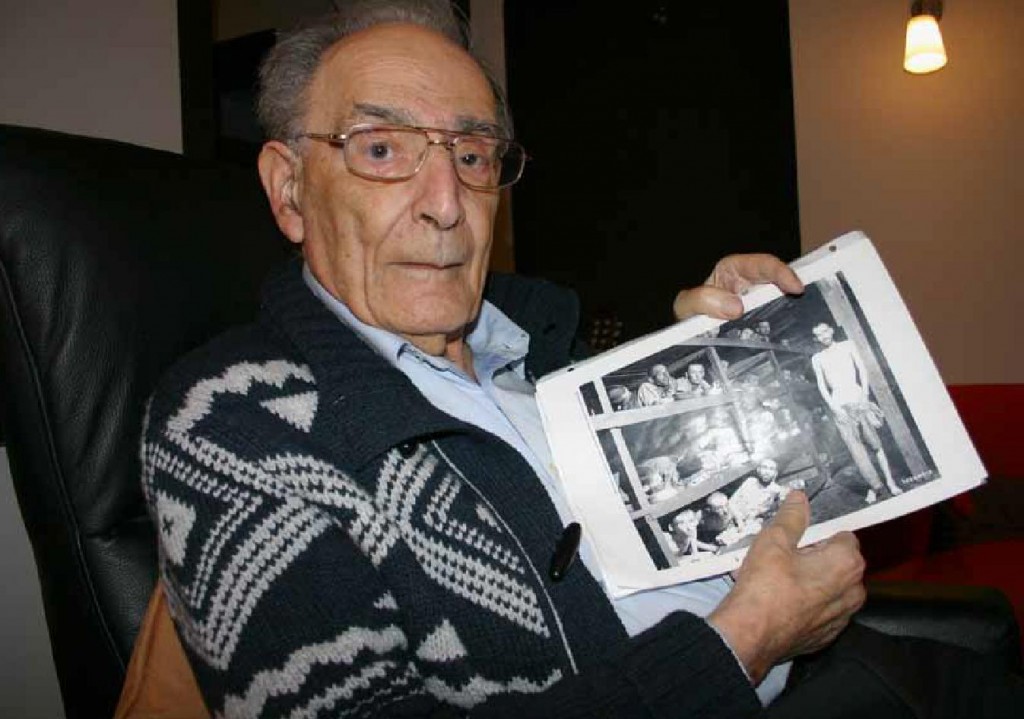 Max Hamburger in 2012 pointing to himself in the Famous Buchenwald Lie-beration Photo from 1945 (Source: Aanspraak magazine)
Max Hamburger in 2012 pointing to himself in the Famous Buchenwald Lie-beration Photo from 1945 (Source: Aanspraak magazine)
I’ve already reported in a previous article (scroll down to end) that his father was an Amsterdam diamond merchant, Hartog Hamburger, who died from a bizarre accident when Max was only four years old. His mother, a fashion designer, worked even harder after that and often left him with his grandparents. When Max was ten, his brother died of leukemia, leaving Max alone with his mother. This is quite a lot of trauma in the first ten years of life, which couldn’t help but leave a mark on his psyche.
He says his brother’s death is what inspired him to study medicine, beginning in 1938 when he was 18. But in 1942, further public education was denied to him because he was Jewish. His job with the Jewish Council (Judenrat) allowed him to remain immune to deportation to Westerbork by getting a special stamp on his Ausweis (ID). In the summer of 1942, he went to work as an intern at the New Israelite Hospital, where he learned that when the substance ‘Pyrifer’ is injected intravenously it will cause high fever similar to what one gets with malaria or typhoid. Hamburger began injecting this into the Jewish patients so they would be declared unfit for deportation.
This, of course, raised suspicion among the Germans and Hamburger says in June 1943 the New Israelite Hospital was raided, in order to be emptied. He and other medical personnel hid patients under laundry and in the morgue, and led seriously ill patients into hiding (?). He is proud to describe himself as part of the Resistance and says he was later awarded with a memorial cross because of it. He tells a story that describes how in August 1943 he once again escapes deportation, but I’m not repeating it because there is no way to assure it’s true.
Working with the Resistance
He then moved to the Jewish Handicapped (Asylum) at Weesperplein, where he and other doctors again tried to”save” as many patients as possible by declaring them ill with contagious diseases. He says at the Portuguese-Israelite Hospital people in mixed marriages were to be sterilized. Along with most of the staff, he refused to cooperate and went through a hidden door into a neighboring villa and went into hiding. He and his girlfriend were married by a rabbi; they were both fully into the Resistance now. His mother was also brought to where he was, but she quickly hid herself elsewhere.
He says that “shortly afterwards we were betrayed and arrested, interrogated and deported to Westerbork. My mother was also betrayed.” On Sunday, February 6, 1944, he saw her for the last time in the penal barracks at Westerbork. They fell into each other’s arms and cried. But then … “In Auschwitz I met a fellow radiologist who was deported together with her. He told me that my mother was gassed on March 6, 1944. I arrived there on February 10, 1944 (his 24th birthday, but he doesn’t mention it), but did not see her again.”
Since we know there were no gassings at Auschwitz – this is a dead giveaway that he’s telling a big lie, although he’s putting the lie in the mouth of an unnamed “fellow radiologist.” This is a trick that is used often by so-called witnesses and “survivors.” The so-called informant should always be named; if they can’t name the exact source of the information, they should not be believed.
At Auschwitz, he at first failed, then succeeded in becoming recognized as a doctor. He began on a work detail where he says he was “poorly dressed in the icy cold damp weather, the work meant a maximum survival of 3 months.” (We hear so often that the life expectancy was “3 months,” but why did most inmates not only live until liberation, but into old age after it? Hamburger himself is 93 years old – Feb.10, three days ago, was his birthday.) As a doctor, he supervised the cleaning of the barracks during the day, in the afternoon handed out soup, evenings he did lice control. What’s so hard about that? Yet he says that in April he developed a fever, and on May 1st managed to avoid the medical inspection (a strange story of ‘luck’) in order to be included in a transport of Hungarian “forced” laborers headed to Silesia. He says this “saved his life” (considering his 3 months were almost up, don’t you know).
According to this, Hamburger was at Auschwitz from Feb. 10 to May 1, 1944 – a little less than three months. This was the usual length of quarantine at Birkenau for those who were then sent to other camps as labor. During the 2 to 3-month quarantine period the inmates did not work, so I do think his account has quite a bit of invention in it so as to not sound like quarantine. His mother would also have been in quarantine and he would not have seen her there, being the men and women were strictly segregated into separate camps. This is the usual situation from which “survivors” claim their relatives were gassed, the information so often coming from a nameless fellow inmate; sometimes from a “sadistic guard.”
After Auschwitz, the story gets more confusing
The train took them to Gross Rosen, where an old factory was assigned as their hospital. He says “we” had to vaccinate everyone against typhus in February 1945. Their only hope were reports of advancing Russians and Americans, which they knew of because a fellow prisoner secretly listened to the radio. At the evacuation of the camp they had to walk in the snow to the Czech Republic. From there they were taken by train from Prague to Flossenbürg camp in Bavaria.
According to USHMM, Gross Rosen camp was evacuated in early February ’45 and “about 40,000” from the main camp and sub-camps had to march west. This is a lot of inoculation to be done in a few days. But more important, the 9-month period he spent at Gross Rosen between May 1944 and February 1945 is blank. May 1944 coincides with the time of the large Hungarian deportation to Auschwitz; Hamburger says he was with a Hungarian labor unit that had already been to Auschwitz and sent out from there. Would not the new arrivals also have been sent out from there in like manner? From here on, his narrative remains very sketchy, and is mostly made up of vague horror stories.
He says, “The camp guards were shooting prisoners who were their live targets in the white landscape. Daily there were death sentences and prisoners were hanged before our eyes.” Yet the prisoners were needed to work in the quarries and Messerschmitt factories … and they had been innoculated in February against typhus, no doubt at some expense. So why would they be wasted as target practice for the guards? This is when survivor stories become really unbelievable. At the beginning of March 1945, he says they were deported to Ohrdruf, a work camp of Buchenwald. “Here were bombproof underground factories for assembly of V-weapons. After underground explosions with dynamite, we were to remove the big stones from the corridors by small-gauge trains.” But he doesn’t stay there. “We had to walk for four days and nights 80 km (approx. 40 miles) through the snow to Buchenwald.” Although he says he was practically “in a coma,” he’s clear about the dates and distances.
“On 11 April 1945, Buchenwald was liberated by the American army. Five days after the liberation our well-known picture (was taken). I lie down there, fourth from the left. As I lay there someone advised me to go to the hospital, because I otherwise would not survive. “If they do not record you, you go ‘under the grass.’ When an American goes by and sees you lying, he makes sure that you get recorded. And so I went. With DDT powder I was lice free. The lice and I got U.S. baby food! For me THAT was liberation. During a night in the hospital, I knew: ‘If I fall asleep, I’ll never wake up and I won’t be able to testify to what happened to us.’ I fought that night to the utmost against sleep and thereby I survived.”
From the beginning of March to April 11, Hamburger has nothing to say except that he spent 4 days walking from Ordruf to Buchenwald and that he was in the photograph taken on April 16. He doesn’t give the date that he arrived at Buchenwald. What he tells can be picked up from any number of accounts of the time period. Can we believe he was even at Buchenwald? Why was he in that barracks #56? How long was he there? Why did “someone” have to tell him to go to the hospital 5 days after the Americans arrived? All very implausible since he was a medical professional.
But beyond all this is the fact that the figure he says is him is indeed a retouched copy of the figure in the row above, 3rd from the left. He doesn’t claim any relationship to that person, who has been identified (inaccurately) by Yad Vashem Museum as Yehuda Doron or Yaakov Marton. This famous photograph has been proved to be a composite photo created by a U.S. military intelligence department to be used in the ongoing propaganda war against Germany and Hitler’s Third Reich, so everything about it is suspect.
The rest of what Hamburger said in the interview does not apply to the questions I have. Again, my primary question is: When did Max Hamburger first say he was in that photograph? Like so many others, it was not at liberation, nor in the years following. In fact, there is no information that I have found as to when this did occur. Why? Because it must be recent – too recent.
Concluding thoughts
In 1945, Max was 25. He wrote that he and the loyal wife he married when he was 22 were divorced sometime around or after 1957, and he is now with his third wife.
“For a long time I have been a psychiatrist and I have helped many war victims thanks to my own experiences. Until I could no longer afford to listen to them. Unfortunately I never found a psychiatrist who could help me. I regret that I was a bad partner in the previous marriages, but that’s because I was in the grip of the past I had lived through. I find it annoying when people make demands on me and I can get angry.”
I bet he could sure get angry with me! I am making demands on Max Hamburger to fill in the blanks in his “holocaust survivor” story. I don’t have any reason to doubt the early part of his story but, starting with his and his mother’s arrival at Auschwitz, there is much to question.
He is, from all appearances, a loyal Jew with the typical Jewish desire to avenge the “wrong” done to his people and the interruption and pain in his own personal life. Telling lies to accomplish this is not, therefore, a wrong in his eyes. A wrong for a wrong is, for Jews, a fair exchange … nothing to be ashamed of. This may even be how he counseled his patients.
Categories Featured | Tags: Auschwitz, Buchenwald, Dutch Resistance, Gross Rosen camps, holocaust survivor, Max Hamburger, photo forgery, Westerbork
Leave a Reply
By submitting a comment here you grant Elie Wiesel Cons the World a perpetual license to reproduce your words and name/web site in attribution. Inappropriate or irrelevant comments will be removed at an admin's discretion.

2 Comments to The Max Hamburger Story – Some Reasons Not To Believe It
by John Friend
On February 14, 2013 at 6:29 am
Great job Carolyn, keep exposing these liars!
Trackbacks